Reporter Ed Mendel covered the California Capitol in Sacramento for nearly three decades, most recently for the San Diego Union-Tribune. More stories are at Calpensions.com.
The two big California public pension funds, CalPERS and CalSTRS, are going opposite ways on a controversial investment strategy, hedge funds, that is under fire from a powerful teachers union.
CalPERS announced two years ago that it was eliminating its $4 billion hedge fund program, citing their cost, complexity and one of its own investment principles: “Take risk only when we have a strong belief that we will be rewarded for it.”
CalSTRS adopted a “risk mitigation strategy” last November that will move 9 percent of its investment portfolio into long-term U.S. Treasury bonds and hedge funds with strategies designed to lose less value during recessions.
The different views of hedge funds is one of the biggest separations of investment strategy since CalSTRS, under legislation 34 years ago, took control of the teacher pension fund that had previously been managed by CalPERS.
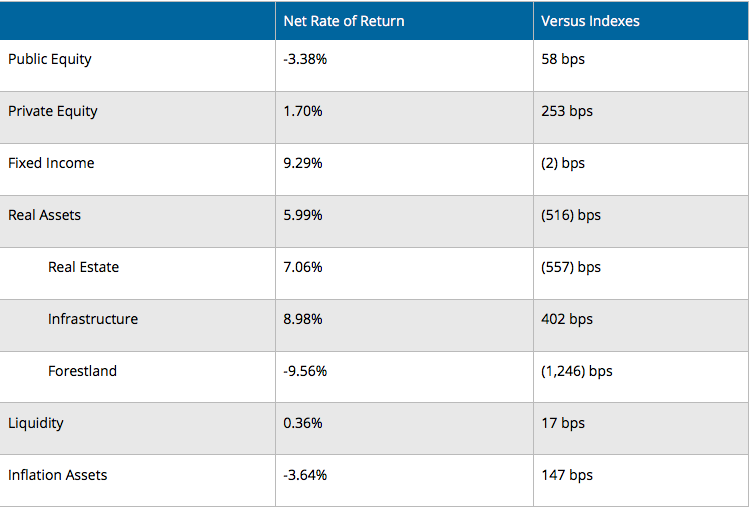
Both funds have similar investment categories — stocks, bonds, private equity, real estate, liquidity, inflation — but with differing ratios and applications of the “ESG” screens (environmental, social and corporate governance) often used by large investors.
When the California State Teachers Retirement System became the manager after the legislation in 1982, the teacher pension fund was $10.9 billion. Now CalSTRS manages a $190 billion fund from its own new 13-story office tower.
It’s across the Sacramento River from the four-block complex where the California Public Employees Retirement System manages a fund worth $301 billion last week. With two of the largest and most impressive state buildings, the pension systems look prosperous.
But both are underfunded, with roughly 70 to 75 percent of the projected assets needed to pay future pensions. They are phasing in painful employer rate increases, while critics say overly optimistic earnings forecasts hide the need for even higher rate hikes.
Both funds have investments with money managers that follow the modern trend of institutional investors to “maximize shareholder value” (recently criticized here) by streamlining businesses, outsourcing jobs and cutting other costs.
As pension funds focus on cutting their own costs in what many expect to be a period of low investment earnings, the 1982 decision creating duplicate staffs and facilities for the two largest U.S. public pension funds may not look like a way to “maximize taxpayer value.”

Hedge funds, typically open only to large investors, use a variety of strategies aimed at out-performing the market and reducing risk. They are known for charging investors high fees and creating a class of wealthy hedge fund managers.
For some, hedge funds are the face of Wall Street greed. One hedge fund strategy, buying defaulted debt at a low price and relentlessly pushing for full repayment, made news this year with huge profits in a $4.65 billion settlement of a 15-year battle with Argentina.
In another debt squeeze, Bernie Sanders, the former Democratic presidential candidate, said last month “billionaire hedge fund managers on Wall Street are demanding that Puerto Rico fire teachers, close schools, cut pensions, and lower the minimum wage so they can reap huge profits off the suffering and misery of the American citizens on that island.”
The distressed debt strategy may be getting much of the attention. But the broader criticism of the thousands of hedge funds, which have a wide range of strategies and nearly $3 trillion in assets, is high costs and poor performance since the financial crisis.
“Hedge funds have underperformed, costing us millions,” Letitia James, an elected public advocate said as the New York City Public Employees Retirement System voted in April to end its $1.7 billion hedge fund program. “Let them sell their summer homes and jets, and return those fees to their investors.”
A Financial Times story in April said public pension funds in several states are considering dumping their hedge funds, nearly two years after CalPERS became the first big pension fund to eliminate hedge funds.
“At the time, many thought it would trigger a wave of redemptions,” the Financial Times said of the CalPERS announcement, “but with public boards tending to be deliberative, it is only now that the wave seems ready to break, hedge fund managers say.”

The CalSTRS decision last fall to increase hedge fund investments caught the eye of Randi Weingarten, president of the American Federation of Teachers, who is in a long-running battle with hedge fund managers, the Wall Street Journal reported last month.
Dozens of wealthy hedge-fund managers are said to have contributed millions to the promotion of charter schools (often opposed by teacher unions if they are not part of a public school system) and the reform of public pensions (often by advocating a switch to 401(k)-style plans common in the private sector).
Three years ago, Weingarten’s union published a list of roughly three dozen Wall Street asset managers that have donated to causes opposed by the union, the Journal said. Teacher pension funds with $1 trillion in assets were advised to use the list when making investment decisions.
“Why would you put your money with someone who wants to destroy you?” Weingarten told the Journal.
A hedge-fund manager who got himself removed from the union’s list, Cliff Asness of AQR Capital Management, remained on the board of the Manhattan Institute, a think tank said by the union to support charter schools and pension reform. The Journal said Weingarten viewed the CalSTRS hedge fund expansion as a chance to apply pressure last fall.
“Dan Pedrotty, an aide to Ms. Weingarten who runs the hedge-fund effort, spoke to a CalSTRS official about Mr. Asness’s continued service on the Manhattan Institute’s board,” the Journal reported. “The official then called Mr. Asness.”
Asness had already decided to leave the Manhattan Institute before receiving the CalSTRS call, his spokesman told the Journal, after reassessing the time that he was spending on non-profit boards.
Last week, a CalSTRS spokesman did not confirm or deny that a CalSTRS official called Asness at the request of the union, pointing instead to an Asness letter on July 4 replying to the Journal story.
“This article implies I left the Manhattan Institute’s board under such pressure, which is false,” Asness wrote. He said, among other things, that he is a supporter of public pensions and the mission of the Manhattan Institute, but not everything written under its banner.
Weingarten’s union published a report last fall, “All That Glitters Is Not Gold,” that criticized hedge funds for high fees and poor performance in recent years. CalSTRS was not among the 11 public pension funds analyzed in the report.
The CalSTRS chief investment officer, Chris Ailman, told CNBC in May that CalSTRS is “not a big fan” of hedge funds and invested in them in 2009-10, after many other pension funds rushed in during 2004 to 2007. He said CalSTRS invested in two hedge fund strategies, not 22 strategies like some of its peers.
Now CalSTRS is looking at a handful of hedge funds that are “counter-cyclical to growth,” Ailman said, and expected to provide some balance during recessions. He said “2 and 20 is dead,” referring to the traditional hedge fund fee of 2 percent of assets and 20 percent of profits as an incentive.
With a long-term risk management strategy to invest 9 percent of its portfolio, Ailman said, CalSTRS has a size advantage in fee negotiations that have already begun. “Our staff has put on their boxing gloves and gone in there and just laid it out, what we are looking for,” he said.