A seemingly routine Capitol Hill hearing got very interesting very fast late last month. The hearing was held by the Ways and Means Social Security Subcommittee and focused on the state of retirement savings in the U.S.
Why was it so interesting? Two of the witnesses, Sylvester J. Schieber and Andrew G. Biggs, insisted that the retirement savings “crisis” in the U.S. is over-hyped. (They were referencing, among other things, the recent government statistics claiming that 20 percent of Americans aged 55-64 had zero retirement savings).
An outpouring of criticism followed, led by Christian Weller, who wrote:
Launched by Chairman Sam Johnson (R-TX), the hearing announcement made reference to retirement income being underreported, implying that families are better off than the data show. Moreover, the witness list included crisis deniers, such as the American Enterprise Institute’s Andrew Biggs, making claims that the number of households inadequately prepared for retirement is largely overstated. Some testimony turned to calls for Social Security benefit cuts. Because, after all, cutting Social Security would theoretically inflict little harm if families are already well prepared for retirement. In reality, families would suffer tremendously from Social Security cuts. Why? Because as a long-standing body of economic research has repeatedly shown, there is indeed a growing crisis.
Schieber and Biggs (who, by the way, are no slouches–you can read their bios at the bottom of this post) quickly took to the blogosphere to explain their position.
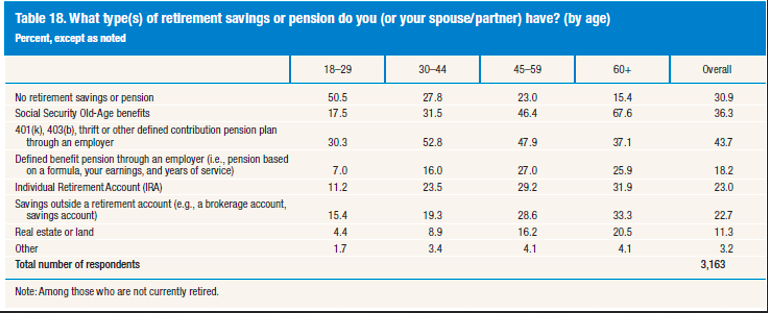
First, they tackled why they disputed the government data, released last week, that suggested one in five Americans nearing retirement had no money at all saved for retirement. From Sheiber and Biggs (S + B):
These [Social Security Administration] publications rely on data from the Current Population Survey, which omits the vast majority of income that seniors receive from IRA and 401(k) accounts and thus makes seniors appear significantly poorer and less prepared for retirement than they actually are.
IRS tax data, which include all forms of pension withdrawals, show that true incomes for middle class retirees receiving Social Security benefits are substantially higher than is believed. The fact that these faulty SSA statistics were cited by the Social Security Subcommittee’s ranking member, apparently without knowledge of the limitations of these data, is evidence that even policymakers’ understanding of retirement security can be improved.
What about National Retirement Research Index’s findings that 6 in 10 Americans are at risk of an insecure retirement? S + B write:
With due respect to the NRRI’s authors, we have already detailed how the NRRI sets a higher bar for retirement income adequacy than most financial advisors and how it ignores the ways that family size and structure play into retirement saving patterns. In addition, the NRRI projects current workers’ future incomes using a one-size-fits-all pattern that ignores the dispersion in earnings that takes place from middle age onward.
This assumption erroneously reduces the “replacement rates” that low earners will receive from Social Security. The NRRI also predicts that traditional defined benefit pension plans will continue to contract, but assumes that future retirees will have no larger IRA or 401(k)s accumulations than those of people who retired prior to 2010. Together, these factors substantially – but erroneously, in our view – increase the share of workers considered to be “at risk” of an insecure retirement.
So who are these people anyway?
Sylvester J. Schieber:
Sylvester J. Schieber is Chairman of the Social Security Advisory Board (SSAB) and a private consultant on retirement and health issues. He retired from Watson Wyatt Worldwide in September 2006 where had served as Vice President/U.S. Director of Benefit Consulting and Director of Research and Information. He holds a Ph.D. in economics from the University of Notre Dame in 1974. He has served on the Board of Directors of the Pension Research Council at the Wharton School, University of Pennsylvania since 1985. Dr. Schieber was a member of the 1994-1996 Social Security Advisory Council. In January 1998 he was appointed to a six-year term on the Social Security Advisory Board.
Andrew Biggs:
Andrew G. Biggs is a resident scholar at the American Enterprise Institute (AEI), where he studies Social Security reform, state and local government pensions, and public sector pay and benefits.
Before joining AEI, Biggs was the principal deputy commissioner of the Social Security Administration (SSA), where he oversaw SSA’s policy research efforts. In 2005, as an associate director of the White House National Economic Council, he worked on Social Security reform. In 2001, he joined the staff of the President’s Commission to Strengthen Social Security.
You can read their entire blog post here.
You can also read the initial blog post, “Yes, There Is A Retirement Crisis”.
It’s a fascinating discussion, although at this moment, it seems to be two men standing alone against a world of data.