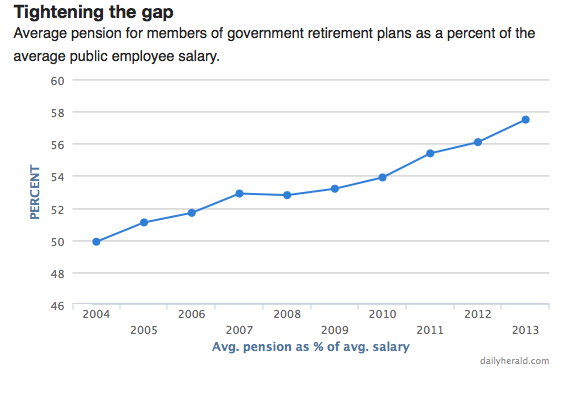
Over the past decade, the average public pension in Illinois has been gradually catching up to the average salary of employees still working.
Critics of increased benefits say this is the result of years of generous salary increases and compounded COLA increases.
Others say that increased pensions are simply the result of higher public sector salaries, which Illinois needs to pay in order to retain good employees.
The Daily Herald reports:
The average 2013 pension was $31,674 for retirees in nine statewide and metropolitan Chicago public pension systems for government workers, teachers, legislators, judges and university professors, a Daily Herald analysis shows. That’s 60 percent of the $55,120 average salary for pension fund members who are still working.
Ten years ago, the average pension was less than half of the average salary.
…
The narrowest gap between average salary and average pension is for members of retirement systems where advanced degrees and training are required.
In 2013, the average Teachers’ Retirement System pension was 69.4 percent of the average pay for those still working, according to the system’s annual comprehensive financial report.
Judges have the highest average salary — $183,998 — and highest average pension — $105,341.
The gap between average pay and average pension is widest within retirement systems with more transient employees.
The 108,814 local government employees receiving IMRF benefits in 2013 averaged pensions of $13,243. That was 34.8 percent of the system’s $38,059 average salary. However, that’s still a big change from a decade ago when the average IMRF pension was 27.9 percent of the average salary of workers paying into the system.
One lawmaker told the Daily Herald that, although the upward trend is undoubtedly real, the decreasing gap between pensions and worker salaries has slowed over recent years.
“There was a long period of time where there were rapid (pay) raises in the public sector … (and) that growth is tied to the pension formula,” said state Sen. Daniel Biss, an Evanston Democrat who helped sculpt the state’s most recent pension reform plan. “But a lot has changed and we’ve seen a dramatic slowdown, particularly in the last five years.”