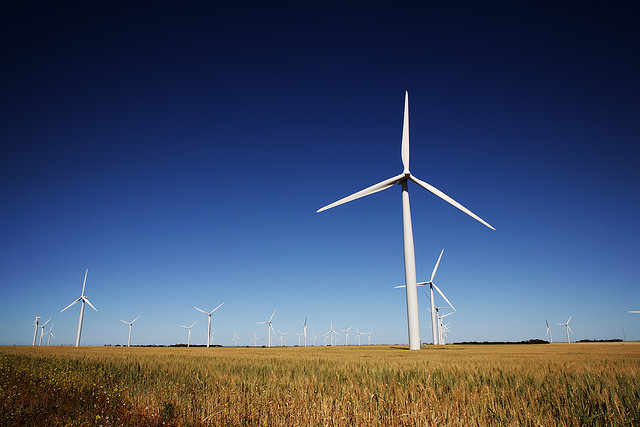
This week, two Canadian pension funds — the Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan Board and the Public Sector Pension Investment Board – teamed up with Spanish bank Banco Santandar S.A. to manage a $2 billion portfolio of renewable energy assets.
Leo Kolivakis of the Pension Pulse blog weighed in on the clean energy bet in a post on Wednesday. The post is re-published below.
______________________
Originally published at Pension Pulse
This is a big deal and I expect to see more deals like this in the future as more European banks shed private assets to meet regulatory capital requirements. In doing so, they will looking to partner up with global pension and sovereign wealth funds that have very long-term investment horizons.
The Spaniards are global leaders in infrastructure projects (Germans and French are also top global infrastructure investors led by giants like HOCHTIEF and VINCI). When it comes to renewable energy, Spain is the first country to rely on wind as top energy source:
Spain is the first country in the world to draw a plurality of its power from wind energy for an entire year, according to new reports by the country’s energy regulator and wind energy advocacy group Spanish Wind Energy Association (AEE).
Wind accounted for 20.9 percent of the country’s energy last year — more than any other enough to power about 15.5 million households, with nuclear coming in a very close second at 20.8 percent. Wind energy usage was up over 13 percent from the year before, according to the report.
The news is being hailed by environmental advocates as a sign that Spain, and perhaps the rest of the world, is ready for a future based on renewables. But the record comes at the end of a very rocky year for Spain’s renewable energy sector, which was destabilized by subsidy cutbacks and arguments over how much the government should regulate renewable energy companies.
Despite the flaws in Spain’s system, the numbers are promising for green energy fans. The renewable push brought down Spain’s greenhouse gas emissions by 23 percent, according to another industry report from Red Electric Espana (REE).
Spain also has one of the largest solar industries in the world, with solar power accounting for almost 2,000 megawatts in 2012. That’s more than many countries but still just a fraction of the energy produced by wind in Spain. In 2013, solar power accounted for 3.1 percent of Spain’s energy, according to the AEE report.
By contrast, the U.S. produced only 9 percent of its energy with renewable sources last year, and wind accounted for only 15 percent of that.
But as the world reaches for more renewables, Spain’s record-breaking year is also a cautionary tale.
Going into 2014, it’s unclear how wind will survive steep government cutbacks.
At the moment, Spain heavily subsidizes its renewable energy sector, which costs billions of dollars in a country still in the depths of a financial crisis. When the country tried to raise individual rates for renewables, people complained bitterly and the government backed off, leaving the country with a nearly $35 billion renewable energy deficit.
The idea that renewables can’t survive without heavy subsidies might be cooling off the market in Spain and elsewhere, bringing the future of renewable growth into question. Global investment in renewable energy slipped 12 percent last year, despite the fact that the European Union and the UN have set ambitious energy goals for the next decade.
It remains unclear how the world will meet those goals given the spending-averse climate of most Western governments, but there’s no doubt they’ll be looking to Spain in 2014 to see if it can be done without going broke.
Indeed, over the summer, Spain’s government dealt a death blow to renewable energy:
In the latest move to draw down Spain’s energy sector debt, Madrid unveiled a new clean energy bill this week that will cap earnings on power plants as well as introduce retroactive actions, earning a quick rebuke from the country’s already ailing renewable sector. According to a Bloomberg report, clean energy “generators will earn a rate of return of about 7.5 percent over their lifetimes,” adding that the rate may be revised every three years and is based on “the average interest of a 10-year sovereign bond plus 3 percentage points.” The new plan will be retroactively applied to programs active from July 2013.
The new plan was presented by Spain’s Industry Minister Jose Manuel Soria as a necessary evolution of the country’s renewable energy subsidy system, which he said would have gone bankrupt if no changes were made. Since taking over the country’s leadership in 2011, the right-leaning Partido Popular has continued to expand on earlier efforts to chip away at the country’s renewable energy support programs, which many critics have called unsustainable. Once hailed as one of Spain’s most viable sectors for strong growth, renewable energy has suffered under a steady restructuring of government support programs.
In addition to slowing the country’s solar and wind growth, the restructuring garnered legal action on the part of both international investors and domestic trade organizations, the latter of which has appealed to the European Commission for some level of protection from tariff and agreement reductions. Early cuts resulted in legal action against Madrid from over a dozen investment funds with stakes in the country’s solar market, adding to the unease of foreign investors.
I can tell you the cash strapped Greek government did the exact same thing on solar projects in Greece. One of the biggest risks in infrastructure projects is regulatory risk as these governments can change regulations at a moment’s notice, severely impacting the projected revenues.
What are the other risks with infrastructure projects? Currency risk and illiquidity risk as these are very long-term projects, typically with a much longer investment horizon than private equity or real estate.
But both PSP and Ontario Teachers’ are aware of these risks and still went ahead with this investments which meets their objective of finding investments that match their long-term liabilities. The Caisse has also been buying wind farms but I am wondering whether they’re blowing billions in the wind.
Interestingly, this is the second major deal between PSP and OTPP this year. In November, I wrote about how they are nearing a $7 billion deal for Canadian satellite company Telesat Holdings Inc.
And on last week, Bloomberg reported that Riverbed Technology (RVBD), under pressure from activist investor Elliott Management Corp., agreed to be acquired for about $3.6 billion by private-equity firm Thoma Bravo and Teacher’s Private Capital.
In fact, Ontario Teachers’ has been very busy completing all sorts of private market deals lately, all outside of Canada, which is smart.
Photo by penagate via Flickr CC