The Kentucky Retirement System has lowered its assumed rate of return on investments from 7.75 percent to 7.5 percent.
The reduced assumption means the system will experience an uptick in unfunded liabilities, but it also ensures a higher annual payment from the state.
The action took place at a Board of Trustees meeting on Thursday. More details from CN 2:
The changes, presented to trustees earlier this year by actuaries with Cavanaugh Macdonald Consulting based on a five-year experience study, lower assumed returns on investments, price inflation, wage growth and wage inflation.
The new assumptions, KRS Executive Director Bill Thielen said, will cost the state roughly $95 million more per year in contributions for the Kentucky Employees Retirement System for state employees in non-hazardous positions during the next biennial budget, based on current plan valuations and payroll figures. They will not take effect until next year’s year-end plan valuations, he said.
[…]
The updated assumptions would push KRS’s unfunded liabilities to $19.5 billion, up from $17.8 billion currently, according to figures presented by Cavanaugh Macdonald Consulting.
At least one of the KRS trustees voiced concerns about approving the new guidelines at Thursday’s meeting. Personnel Cabinet Secretary Tim Longmeyer suggested delaying a vote until January so the board could meet with the governor’s office, legislators and others affected by the change.
“My concern is we don’t live in a bubble, so $95 million a year is a significant uptick,” said Longmeyer, who abstained from voting on the updated assumptions.
KRS Trustee Randy Overstreet, though, urged the board to move forward with the proposal. Nothing would change between now and January, he said.
“I’m thinking that we almost have the responsibility to follow the experts’ recommendations, and you’re right, it’s not a science, but it’s the best information we have to act on and move forward on since we have for the 20 years I’ve been on this board,” Overstreet said.
More context on KRS’ new assumed rate of return, from the Courier-Journal:
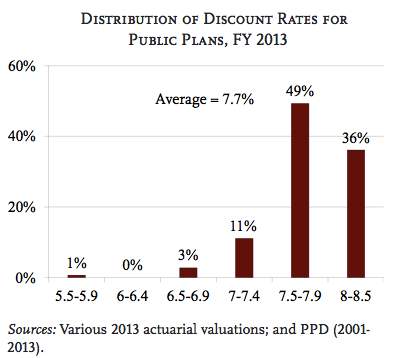
KRS has forecast a 7.75 investment return since 2007. But earnings in KERS non-hazardous averaged only 6.52 percent over the past decade, leading some critics — including lawmakers — to argue for a more cautious outlook.
The National Association of State Retirement Administrators reported that of 126 public retirement plans surveyed in October, 48 assumed a return of 7.5 percent or lower, while 78 assumed a higher rate.
The median rate was 7.75 percent, but more than half have cut their assumption since 2008, the group said.
KRS administers nearly a dozen defined-benefit plans for state workers, including the 21 percent funded KERS non-hazardous plan.








