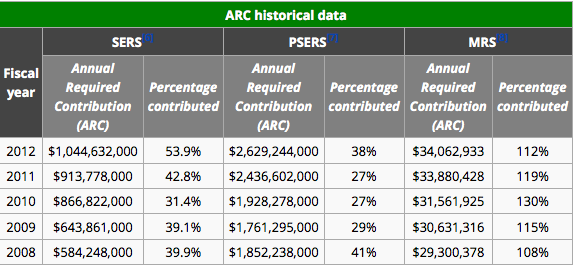
Two Pennsylvania laws have allowed the city of Scranton to short its pension systems by about $10.9 million since 2009 – or over 22 percent of the city’s actuarially-required contributions over that time period.
Scranton used this tactic because the city needed money to plug budget shortfalls elsewhere – but now bigger payments await the financially troubled city in the future.
The laws that allow the practice are called Act 44 and Act 205. More details from the Scranton Times-Tribune:
Act 205 allowed municipalities to reduce their MMOs by employing an accounting tactic known as actuarial smoothing, which spreads out debt and stock market losses over a long period, up to 15 to 30 years.
But the breaks did not stop there.
Scranton also benefited from Act 44, which allowed municipalities with financially distressed pension plans to reduce the MMO by 25 percent for up to six years. Scranton has taken the reduction each year since 2009.
In 2014, for instance, the actuary determined the city needed to contribute $15.7 million,but the Act 44 reduction allowed it to put in just $12.1 million.
The acts were designed to provide temporary relief for municipalities hit by the stock market crash, which caused their MMO’s to skyrocket, said James McAneny, executive director of the Public Employee Retirement Commission. Scranton’s plans were particularly hard hit, losing a combined total of $21.3 million in the crash, PERC records show.
The problem, he said, is putting off the payments only compounded the pension plans’ financial woes.
“It defers the payment but it doesn’t make it go away,” Mr. McAneny said. “The obligation to make the payment is still there . . . If you are putting it off, all you are doing is facing a bigger payment later. If you can’t pay it now, what makes you think you can pay it later?”
Former Mayor Chris Doherty said he knew the city was putting in less than the actuary determined was required, but he said he felt safe doing so because the reductions were state-approved.
“It’s not like a choice I made that I’m going to deliberately underfund it,” Mr. Doherty said. “We didn’t have the money. We funded it at the rate they told us to fund it.”
A state audit earlier this year revealed that Scranton’s pension system could become broke in as soon as 3 to 5 years.