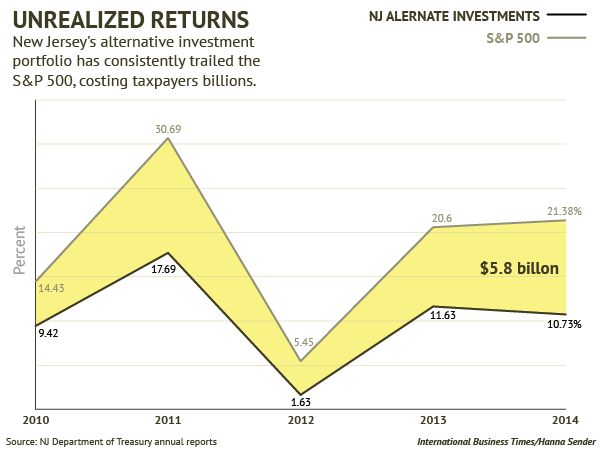
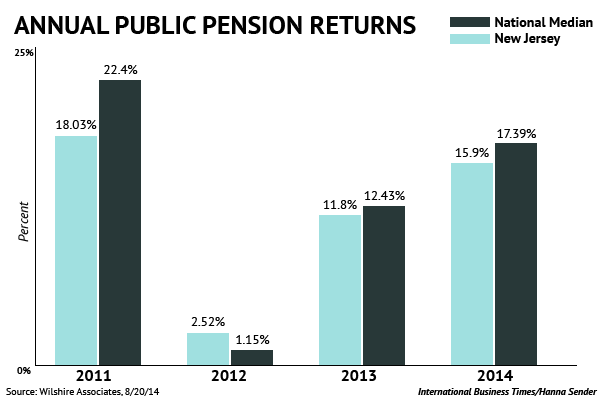
In 2011, politician and businessman Charlie Baker made a $10,000 contribution to the New Jersey Republican State Committee. At the time, he was a partner at General Catalyst, a venture capital firm.
Months later, New Jersey’s pension system gave a contract to General Catalyst to manage the state’s pension money.
After the potential conflict of interest was uncovered by journalist David Sirota, New Jersey launched an investigation into the situation.
But the state is now refusing to release the findings of the investigation. From David Sirota:
Christie officials have denied an open records request for the findings of the investigation.
In a reply to International Business Times’ request for the findings of the audit under New Jersey’s Open Public Records Act, Christie’s Treasury Department said the request is being denied on the grounds that the documents in question are “consultative and deliberative material.” Despite officials’ assurances in May that the probe would take only weeks, the New Jersey Treasury said in September that the investigation is still “ongoing” — a designation the department says lets it stop the records from being released.
IBTimes is appealing the open-records denial to the state’s Government Records Council. Neither Baker nor Christie responded to requests for comment on the issue.
General Catalyst and Baker have denied that Baker had anything to do with persuading Christie officials to invest in the firm. To try to verify that assertion, IBTimes filed a separate request for any General Catalyst documents sent to the New Jersey Department of Treasury prior to its investment. Those documents would show whether General Catalyst specifically promoted Baker’s involvement in the firm when pitching its investment to New Jersey.
Christie officials are pushing back the due date to release those documents to Nov. 6 — two days after the election.
New Jersey has fallen into a habit recently of denying public records requests. From the International Business Times:
The denial letters to IBTimes come only weeks after the Associated Press documented a spike in the number of open records requests that have been rejected by Christie officials. Since 2012, Christie’s administration has paid out $441,000 in taxpayer funds to reimburse open-records plaintiffs who were unlawfully denied access to government records.
“Open records requests to the executive branch have become even more highly politicized than usual,” said Walter Leurs, president of the New Jersey Foundation for Open Government. “These documents are subject to the open records laws and they are supposed to be disclosed within seven days, so this is stonewalling. They know that any lawsuit challenging the denials wouldn’t be heard for 60 days — which is well after the election.”
Charlie Baker has denied he worked for General Catalyst when New Jersey decided to give the firm a contract. But the firm’s website listed him as a partner, and Baker himself called himself a partner in documentation related to his $10,000 contribution back in 2011.