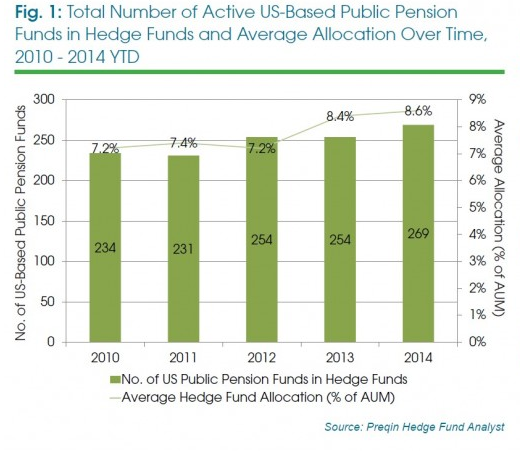
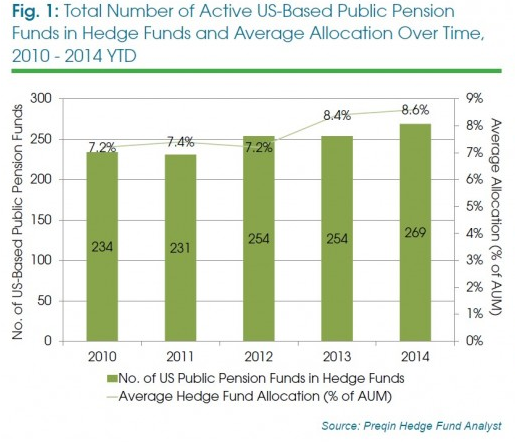
 In recent years, hedge funds have solidified themselves as a big part of pension portfolios by two measures:
In recent years, hedge funds have solidified themselves as a big part of pension portfolios by two measures:
1) More pension funds than ever are investing in hedge funds
2) Those pensions are allocating more money towards hedge funds than ever before
That bears itself out in the above graphic, and this next one:
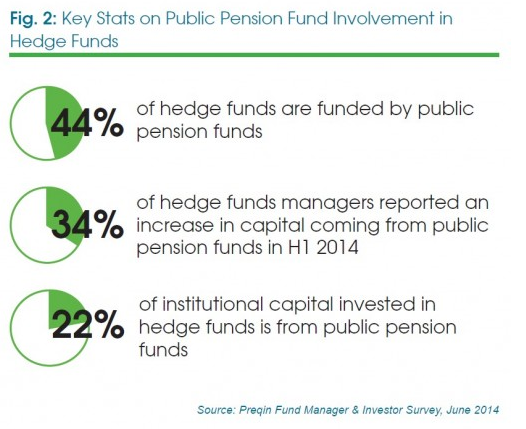 A recent Preqin report had this to say about the numbers:
A recent Preqin report had this to say about the numbers:
“There are more US public pension funds than ever before allocating capital to hedge funds, and these investors are investing the most they ever have in the asset class. Public pension funds have increasingly recognized the value of hedge funds as part of a diversified portfolio, and although CalPERS’ withdrawal from the asset class will spark some investors to look more closely at their current allocation model, the importance of hedge funds as a source of risk-adjusted returns for these investors is likely to continue to prove attractive for US retirement schemes.
Preqin’s recent research highlights that investors are not using hedge funds to produce outsized returns, but instead to produce uncorrelated, risk-adjusted returns. Over short and longer time frames, hedge funds have in general met investor needs for risk-adjusted returns. However 2014 has been a period of relatively turbulent returns when looking at Preqin’s monthly benchmarks; in times like this, investor calls for changes in fee structures and better alignment of interests become more vocal, and this clearly has had an impact on CalPERS’ decision.”
Chart Credit: Preqin