CalPERS announced this week that it was cutting down the number of private equity managers it employs – possibly by as much as two-thirds.
The change comes in the name of cutting costs. A similar rationale was used when the pension fund decided to exit its entire hedge fund portfolio last year.
But unlike hedge funds, private equity will remain a significant part of CalPERS’ investment strategy going forward.
From the New York Times:
Calpers is not planning to significantly reduce its allocation to private equity, though it may redistribute it, Joe DeAnda, a Calpers spokesman, said in an email. He said the pension fund may increase its allocation to individual private equity managers as it culls the number of managers.
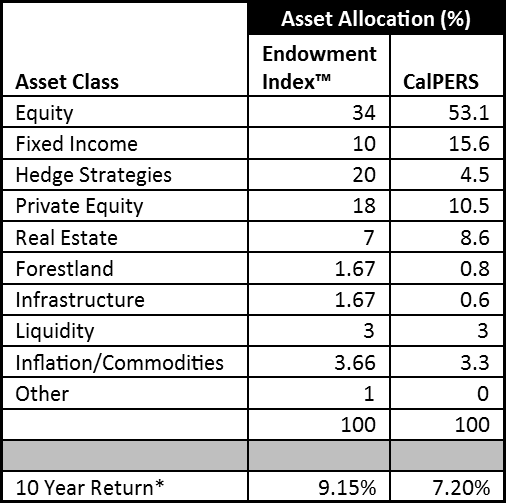
As of October, Calpers had $31.2 billion invested in private equity, or about 10.5 percent of its overall portfolio, according to the most recent disclosure. It aims to have 10 percent of its portfolio allocated to the strategy.
[…]
When it comes to private equity, Calpers is also trying to reduce costs. But its approach is more subtle.
Réal Desrochers, the pension’s head of private equity since 2011, announced in late 2013 that Calpers aimed to reduce the number of managers to as few as 100. (DealBook reported on it here.)
In a presentation to the Calpers investment committee in December that year, Mr. Desrochers discussed his review of the pension fund’s private equity portfolio. It included 389 managers at the time.
“I think this portfolio should have — given the size where we are — it should be probably around 100, 120, something like that,” Mr. Desrochers said. (See the 29:15-minute mark in this video.)
In other words, this move has been in the making for a long time.
CalPERS allocates about 10 percent of its assets towards private equity.
Photo by rocor via Flickr CC License