Two trends have been building in recent years, and now they are set to collide: on one hand, employers are increasingly shifting workers into defined-contribution plans. On the other, workers are becoming more likely to move between companies numerous times over the course of their working lives. Those trends together are bound to butt heads. Canover Watson writes:
As with many other major Western economies, the US in recent decades has seen its pensions landscape shift away from “defined benefit” (DB) to “defined contribution” (DC) plans […] The move from the former to the latter is unmistakable. […] DB plans tend to favour long-tenured employees, are not transferred so easily between employers, and so are less suited to a highly mobile workforce.
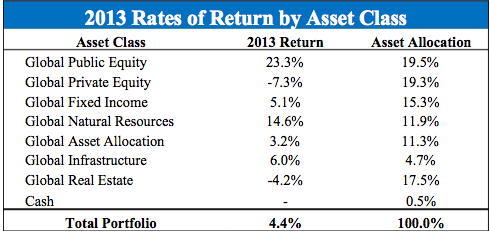
The effective result of this transition is that individual savings accounts, originally intended to supplement DB plans, have ended up supplanting them. This has rendered the question of optimizing returns from investments a cornerstone of the pension debate, as these returns now directly dictate the employees’ eventual retirement income.
Present and future retirees’ exclusive dependence on 401(k)s has upped the ante for all stakeholders–these funds need to achieve consistent returns required to provide liveable, income during retirement. But different funds and managers operate in different ways, and those differences are amplified when a worker switched employers numerous times. From Canover Watson:
What is required is the consistent application of a single accounting approach to underpin accurate portfolio valuations. The answer to achieving this, as with many things in our modern world, lies partly with technology and automation-namely the adoption of a master accounting system at the level of the pension fund.
The shift to DC plans and the multimanager model, both represent a step forward: the creation of a more sustainable, efficient system for ensuring that citizens are able to generate sufficient income for their retirement years. Yet, unless these changes are met with a more sophisticated, automated approach to accounting, pension returns ultimately will be short-changed by the march of progress.
To read the rest of this journal article, click here.
The article was published in the Journal of Pension Planning and Compliance.
Photo by