Canada’s pension plans were among the first in the world to invest in infrastructure, and they remain the most prominent investors in the asset class.
Are there any lessons to be learned from Canada when it comes to infrastructure investing? Georg Inderst, Principal of Inderst Advisory, thinks so.
In a recent paper in the Rotman International Journal of Pension Management, Inderst dives deep into Canada’s infrastructure investing and emerges with some lessons to be considered by pension funds around the world.
The paper, titled Pension Fund Investment in Infrastructure: Lessons from Australia and Canada, starts with a short history of Canadian infrastructure investing:
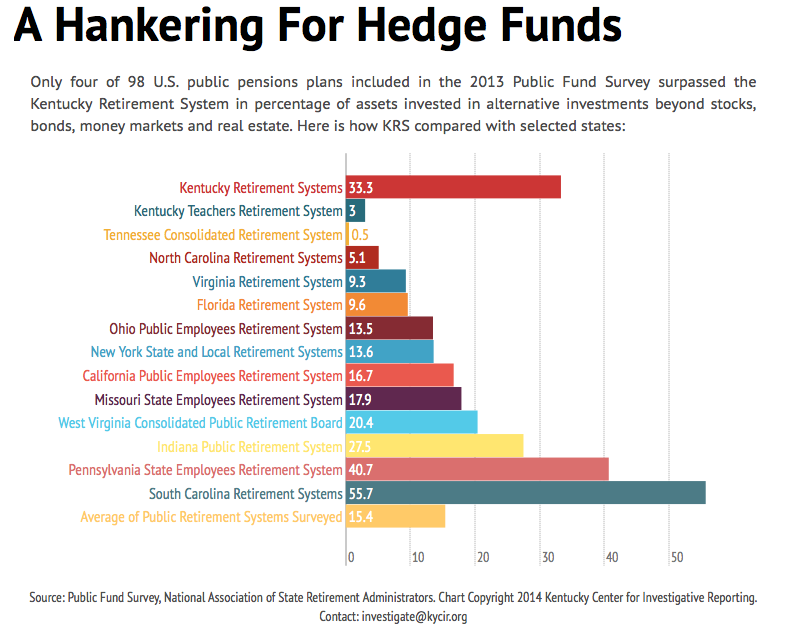
Some Canadian pension plans, notably the Ontario Teachers’ Pension Plan (OTPP) and the Ontario Municipal Employees Retirement System (OMERS), were early investors in infrastructure in the late 1990s and early 2000s, second only to Australian superannuation funds. Other funds followed, and the average allocation has been growing steadily since, reaching C$57B by the end of 2012 (5% of total assets). Here, too, there is a heavy “size effect” across pension funds: bigger pension plans have made substantial inroads into infrastructure assets in recent years (see Table 2), while small and medium-sized pension funds have little or no private infrastructure allocation.
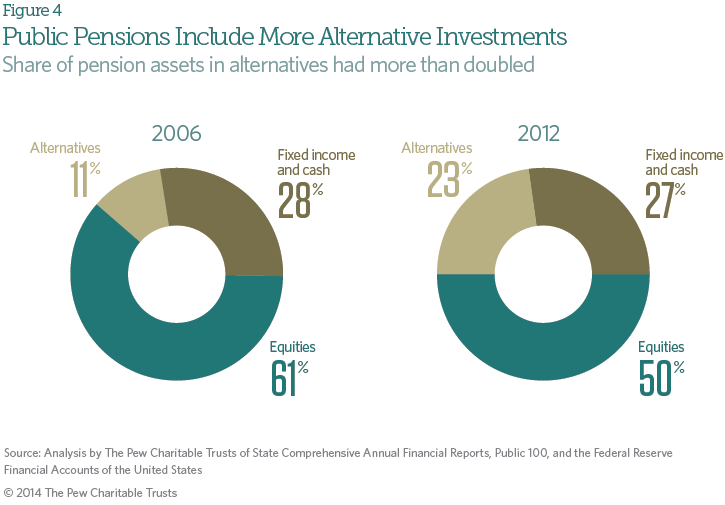
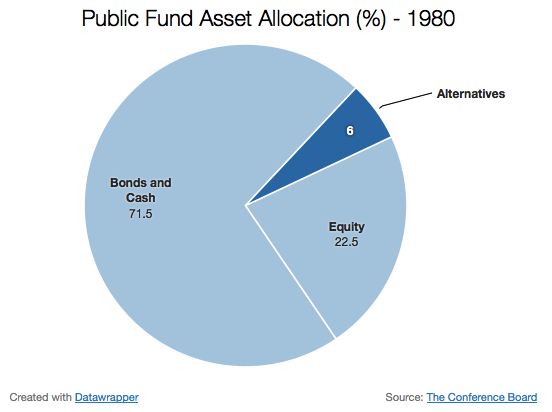
The main driver for infrastructure investing appears to be the wish to diversify pension funds’ assets beyond the traditional asset classes. While Canadian pension funds have been de- risking at the expense of listed equities, regulators have not forced them into bonds, as was the case in some European countries. Real estate and infrastructure assets are also used in liability-driven investing (LDI) to cover long-term liabilities.
Canada frequently makes direct investments in infrastructure, an approach that is now being tested by pension funds around the world. From the paper:
According to Preqin (2011), 51% of Canadian infrastructure investors make direct investments, the highest figure in the world. This approach (known as the “Canadian Model”) has attracted considerable attention around the world, for several reasons:
• lower cost than external infrastructure funds
• agency issues with fund managers
• direct control over assets (including entry and exit decisions)
• long-term investment horizon to optimize value and liability matching
This direct approach to infrastructure investment must be seen in the context of a more general approach to pension plan governance and investment. Notable characteristics of the “Maple Revolutionaries” include
• Governance: Strong governance models, based on independent and professional boards.
• Internal management: Sophisticated internal investment teams built up over years; the top 10 Canadian pension plans outsource only about 20% of their assets (BCG 2013).
• Scale: Sizable funds, particularly important for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Potential challenges for the direct investing approach include insufficient internal resources, reputational and legal issues when things go wrong, and the need to offer staff market-based compensation in high-compensation labor pools.
Despite these challenges, however, the direct internal investment approach of large Canadian pension funds is now being tried in other countries. Other lessons from the Canadian experience include the existence of a well-functioning PPP model, a robust project bond market, and long-term involvement of the insurance sector.
Finally, the paper points to some lessons that can be learned from Canada:
Lessons learned include the following:
• Substantial infrastructure investments are possible in very different pension systems, with different histories and even different motivations.
• Infrastructure investment vehicles can evolve and adjust according to investors’ needs. In Australia, listed infrastructure funds were most popular initially, but that is longer the case.
• Pension plan size matters when investing in less liquid assets. Private infrastructure investing is driven primarily by large- scale funds, while smaller funds mostly invest little to nothing in infrastructure. In Australia, two-thirds of pension funds do not invest in unlisted infrastructure at all.
• Asset owners need adequate resources when investing in new and difficult asset classes. Some Canadian plans admit that their own estimates of time and other inputs were too optimistic at the outset.
• New investor platforms, clubs, syndicates, or alliances are being developed that should also attract smaller pension funds, such as the Pension Infrastructure Platform (PIP) in the United Kingdom or OMERS’ Global Strategic Investment Alliance (GSIA). However, industry experts stress the difficulties of such alliances with larger numbers of players, often with little experience and few resources. Decision time is also a critical factor.
The full paper offers much more insight into Canada’s approach as well as Australia’s. The entire paper can be read here.