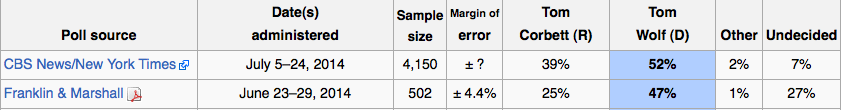The election for Pennsylvania governor draws closer, but pension reform seems farther away than ever.
Gov. Tom Corbett has made pension reform his campaign cry. But he remains down in the polls as the urgency to pass pension reform dwindles around him—both from inside and outside the capitol. ABC 27 reports:
A typical late-August day and all is quiet at the Capitol.
But this silence is not golden for a governor who has criss-crossed the state begging/cajoling/shaming/pleading with lawmakers to give him pension reform.
“We have a bill out there right now that I want the legislature to come back and finish,” Governor Tom Corbett said a week after the legislative exodus in early July.
The governor has poster boards calling pensions a $50 billion problem that will burden future generations of Pennsylvanians.
There is disagreement among lawmakers on how to fix pensions and disagreement as to whether there’s even a problem.
“The word crisis is being used for ideological reasons, not any mathematical reasons,” insists Senator Rob Teplitz (D-Dauphin).
Teplitz, and most Democrats, believe the problem was created by the state failing, for years, to pay what it owed toward pensions and now it’s time to pay the consequences and pay up.
“It does feel more painful,” Teplitz said. “But just like any family that delays making its credit card payment, sooner or later you gotta make that payment.”
There’s no urgency among lawmakers because there’s not urgency among voters, said one pollster. Education funding is on the mind of the electorate, not pension reform. From the Philadelphia Daily News:
[Pollster Terry] Madonna said that for voters the pension-funding increase is “not something they relate to,” while Pennsylvania school districts raise local property taxes, lay off staff and curtail programs.
Other high-level observers agree that voters aren’t as engaged on pension issues. From ABC 27:
“It’s something that the public still hasn’t been able to get its arms around,” said Lowman Henry, a conservative commentator with the Lincoln Institute. “As a result, you’re not seeing that type of collective pressure on lawmakers that is going to push them to make what are very difficult decisions in an election year.”
The latest poll shows Corbett trailing his Democratic challenger, Tom Wolf, by 25 points. Wolf currently holds 49 percent of the vote, while Corbett holds 24 percent. Twenty-five percent of voters remain undecided.